How to Build a TAM for Any Target Market
The Ultimate B2B List Building Guide
Blogby JanApril 21, 2025

Ever spent weeks building a target list only to realize you're missing half your market? The average sales team wastes 30+ hours monthly on manual list building, often ending up with incomplete data anyway.

When defining your Total Addressable Market (TAM), the Pareto principle holds true: reaching 80% of your market is relatively simple. However, capturing the remaining 20% is significantly more challenging and often not worth the extra effort.
In this guide, I'll walk you through how to efficiently build comprehensive TAM lists for virtually any target market using a strategic approach that combines multiple data sources. No more guesswork, no more incomplete lists, just a systematic process that works for everything from yoga studios to SaaS companies.
Understanding the TAM Building Pipeline
Building an effective TAM isn't about using a single data source—it's about strategically combining multiple sources to maximize your coverage while maintaining quality. Here's the essential pipeline that Databar.ai users implement to build comprehensive lists for their campaigns:
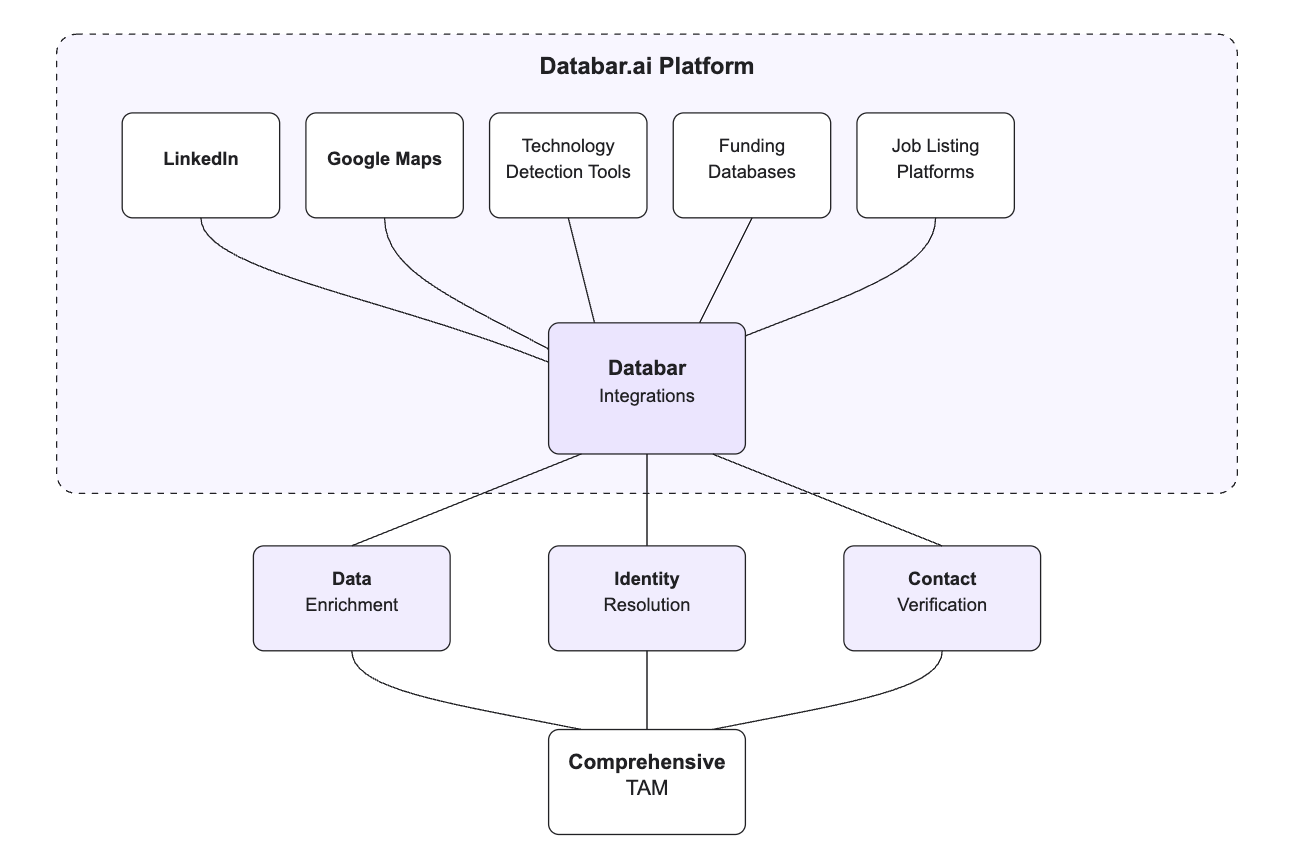
This pipeline connects multiple data sources, enrichment tools, and verification methods to ensure you capture as much of your market as possible. By leveraging Databar.ai's 90+ integrated databases, users can create lists that would be impossible with any single data source.
The key insight? Different data sources excel at different types of businesses. LinkedIn-based datasets work well for professional services, while Google Maps-based tools are better for local businesses. By understanding which tools to use for which markets, you can dramatically improve your coverage.
Choosing the Right Data Source for Your Target Market
The first critical decision in building your TAM is determining where your target audience is most likely to have a presence. This fundamentally breaks down into two main categories:
LinkedIn-Present Businesses
If your target market consists of companies where decision-makers typically maintain LinkedIn profiles (B2B software, professional services, enterprise companies), your primary data sources should include:
- Professional databases with LinkedIn-sourced data
- Technology detection tools like Builtwith or Wappalyzer
- Investment databases like Crunchbase or Owler
For these businesses, you'll get high-quality data with professional emails, accurate job titles, and company information from sources that primarily use LinkedIn as their data foundation.
Local/Small Businesses
If you're targeting businesses that don't have a strong LinkedIn presence (restaurants, yoga studios, local contractors), you'll need different sources:
- Google Maps extractors
- Facebook pages extractors
- Business directories like Yellow Pages
- Local listing aggregators
- Industry-specific directories
For these businesses, you'll often need to use AI-powered tools to extract contact information from websites, as the data won't be readily available in professional databases.
The Databar.ai Advantage: 90+ Integrated Databases
Databar.ai integrates over 90 databases to solve exactly this problem. Instead of jumping between platforms, you can access all these data sources through a single interface, making comprehensive TAM building possible without the technical hassle.
This integrated approach means you're not limited to a single data perspective. When one source misses a business, another picks it up—giving you the most complete view of your market possible.
Building TAMs for Specific Target Markets: Real Examples
Let's walk through how to build TAMs for specific target markets that commonly use cold email outreach, showcasing the strategy in action:
1. HR Directors at High-Growth Startups
The Challenge: Many high-growth startups have just recently created dedicated HR positions.
The Strategy:
- Begin with funding databases to identify startups that recently raised Series A or B funding
- Use LinkedIn-based tools to identify companies that have recently added HR leadership roles
- Add companies with active job listings showing rapid expansion
- Filter for companies between 50-250 employees (typically when formal HR roles emerge)
- Verify HR director information through company websites and LinkedIn
- Test email formats to ensure deliverability
This strategy targets companies at exactly the growth stage when HR leaders are actively seeking new solutions and are receptive to cold outreach.
2. Mid-Market Manufacturing Companies Using Outdated ERP Systems
The Challenge: Identifying manufacturers specifically running legacy software requires technical signals.
The Strategy:
- Begin with manufacturing industry databases filtering for companies with 50-500 employees
- Use technology detection tools to identify companies using older ERP platforms
- Add companies posting job listings mentioning legacy systems
- Include companies from industry forums discussing ERP migration challenges
- Enrich with IT decision-maker contact information
- Verify company size and technology use before final outreach
This approach combines industry data with technology signals to identify prospects at the exact point where they're likely considering system upgrades.
3. Commercial Real Estate Brokers in Texas
The Challenge: Identifying active commercial brokers who aren't part of major national firms.
The Strategy:
- Begin with professional databases filtering for real estate roles in Texas
- Supplement with local real estate association membership lists
- Add brokers who have recently listed commercial properties on platforms like LoopNet
- Use AI to extract broker contact information from brokerage websites
- Clean and verify emails using validation tools
The key insight here is that combining transaction-based data (recent listings) with professional associations creates a more complete picture of active brokers who regularly respond to cold outreach.
4. Dental Practices Not Currently Using Online Scheduling
The Challenge: Finding practices that need online scheduling requires identifying a technological gap.
The Strategy:
- Start with healthcare provider databases filtered for dental practices
- Use technology detection to identify practices without scheduling software
- Add practices from Google Maps data in target regions
- Test websites with AI to confirm absence of online booking features
- Extract office manager and dentist contact information
- Verify emails using validation services
This strategy demonstrates how to identify service gaps by combining industry listings with technology absence detection—perfect for solutions providers using cold email to reach these prospects.
5 Rules for Building a Comprehensive TAM
Building a truly comprehensive TAM that captures your market without wasting time on dead ends requires a systematic approach. Let me break down each rule with actionable insights:

1. Determine platform presence first
Always start by asking: "Where do these businesses and decision-makers have a digital presence?" This fundamental question determines your entire data collection strategy.
Why it matters: I've seen teams waste weeks scraping LinkedIn for local bakeries that barely have websites, let alone professional profiles. Conversely, others try finding enterprise software executives through Google Maps. Both approaches are doomed.
How to implement: Run small test searches across different platforms before committing to a full data collection strategy. If 8 out of 10 test searches yield results on a particular platform, that's your primary source. If you're getting under 30% hit rates, you need to pivot to another source.
2. Start with the broadest possible list
Begin with the widest definition of your target market, then narrow down. It's easier to remove irrelevant entries than to find missing ones.
The practical approach: Cast a wide net using broad industry codes or categories, then apply filters to refine. For example, when targeting healthcare technology, start with all healthcare providers and all technology companies, then find the intersection.
Data points to collect early: Even when you'll eventually need specific criteria, always gather basic firmographic data first (company name, location, size, revenue range). This foundation makes further refinement much more efficient.
3. Use industry-specific databases where possible
Industry-focused data sources often provide better coverage and more accurate information than general business databases.
Real numbers: In my experience, industry-specific databases typically capture 35-40% more relevant businesses compared to general databases. They also provide 2-3x more industry-specific data points that improve targeting.
Where to find them: Beyond the obvious (like construction directories for builders), look for:
- Industry association member lists
- Conference attendee directories
- Regulatory filings specific to the industry
- Trade publication subscriber data
- Certification bodies and their member directories
4. Combine technology and industry filters
When targeting businesses based on both industry and technology use (like "e-commerce companies using Webflow"), always use both filters to refine your list.
The sequence matters: Start with the broader filter (usually industry) to create your initial pool, then apply technology filters. This approach is more efficient than beginning with technology users and then trying to determine industries.
Hidden signals: Look beyond explicit technology markers. For example, businesses using certain payment processors, specific API calls, or particular hosting services can indicate technological sophistication even when the primary tech stack isn't visible.
5. Let AI handle custom criteria
For criteria that standard databases don't track (like specific service offerings), use AI tools to analyze websites and extract this information.
Practical application: Set up AI tools to scan for:
- Specific service mentions on website pages
- Pricing indicators for market positioning
- Content topics that signal particular specialties
- Customer types featured in case studies
- Specific pain points mentioned in blog content
Validation approach: AI extractions require validation. Use a sample-based approach—manually verify 10-15% of AI-extracted data points to confirm accuracy before relying on them for full-scale targeting.
Common TAM Building Mistakes to Avoid
As you build your target lists, watch out for these common pitfalls:
Relying on a single data source
No single database has complete coverage. Always combine multiple sources for comprehensive results.
Ignoring data freshness
Business data decays at roughly 30% annually. Always check when information was last updated and prioritize recent data.
Skipping verification steps
Clean data is more important than big data. Always verify critical information, especially for high-value targets.
Chasing 100% coverage
The quest for perfect coverage often leads to diminishing returns. Focus on quality over completeness.
Neglecting local businesses
Many B2B tools focus on companies with strong online presence, missing local businesses that might be perfect customers.
Building Better TAMs with Databar.ai
Traditional list building requires juggling multiple platforms, manual exports/imports, and tedious deduplication. Databar.ai solves this by integrating 90+ data sources into a single platform that allows you to:
- Access all major business databases through one interface
- Build complex, multi-source TAMs without technical skills
- Automate verification and enrichment workflows
- Maintain data freshness with scheduled updates
- Deploy your lists directly to outreach platforms
This integrated approach doesn't just save time—it creates fundamentally better TAMs by combining data sources in ways that would be impractical manually.
The Bottom Line: Strategic TAM Building
Building an effective TAM isn't about finding every single potential customer—it's about efficiently identifying enough high-quality prospects to fuel your growth. By understanding where your target audience maintains a digital presence and strategically combining the right data sources, you can build comprehensive lists for virtually any market.
Remember, the goal isn't perfection but practicality: a good-enough TAM that you can start working today will generate more revenue than a perfect one that takes months to build.
Ready to bring your list building process to the next level? Try Databar.ai free today and see how our 90+ integrated data sources can give you the most comprehensive view of your target market available.
Related articles

Context Engineering for GTM Teams: The Complete Guide
Turn Your GTM Approach with AI That Knows Your Audience and Plays by Your Rules
by Jan, February 27, 2026

How to Build Claude Code Skills for GTM (With Templates)
Master GTM Automation with Step-by-Step Claude Code Skill Templates
by Jan, February 26, 2026

Claude Code for GTM Engineers: The Practical Guide to Building Campaigns in 2026
How GTM engineers can save time and boost accuracy with Claude Code
by Jan, February 25, 2026

Claude Code for RevOps: How Revenue Operations Teams Are Using AI Agents to Fix CRM Data, Automate Pipeline Ops & Build Systems
Using AI Agents to Fix CRM Data and Streamline Revenue Operations for Scalable Growth
by Jan, February 24, 2026