Chief Sales Officer: Complete Role Guide for Modern Revenue Leaders
How Modern Chief Sales Officers Drive Revenue Growth Through Strategic Leadership and Data-Driven Insights
Blogby JanAugust 05, 2025

The Chief Sales Officer (CSO) role has evolved from a traditional sales manager position into one of the most strategic and influential positions in modern business. With companies experiencing 19% faster revenue growth when sales, product, and marketing teams are properly aligned, the CSO has become the architect of this critical coordination.
Unlike a decade ago, today's CSO operates in a data-driven environment where artificial intelligence and automation are reshaping the entire sales landscape. By 2027, Gartner predicts that 95% of seller research workflows will begin with AI, up from less than 20% in 2024. This transformation demands a new breed of sales leader who combines strategic vision with technological expertise.
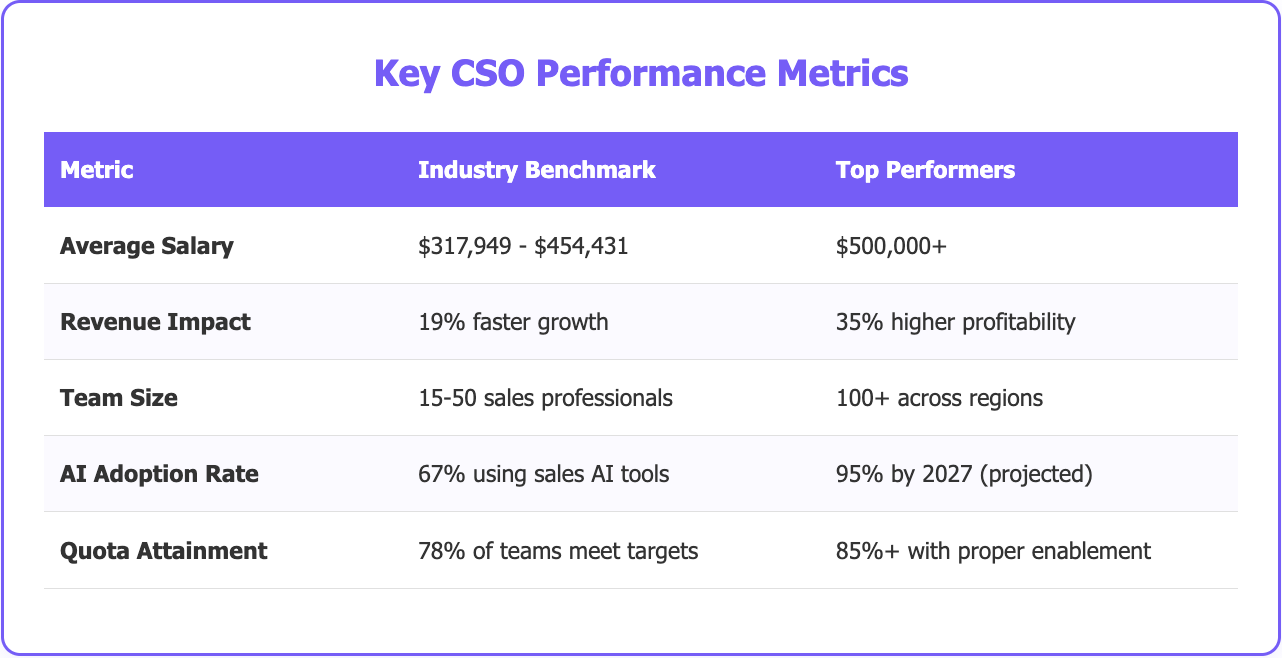
What is a Chief Sales Officer?
A Chief Sales Officer is the senior executive responsible for developing, implementing, and optimizing a company's entire sales strategy. They lead the sales organization, drive revenue growth, and ensure that sales efforts align with broader business objectives and market opportunities.
The CSO role encompasses setting long-term sales vision and strategy, managing sales teams and performance metrics, driving cross-functional collaboration with marketing, product, and customer success, implementing data-driven decision-making processes, and building scalable sales operations and processes.

Understanding CSO vs. Other Sales Leadership Roles
The distinction between CSO and other sales roles is crucial for organizational structure. While a CSO focuses on strategic, company-wide sales initiatives, a VP of Sales manages day-to-day operations. The CSO plans 3-5 years ahead, whereas the VP of Sales focuses on quarterly and annual targets. In terms of decision authority, the CSO reports to the CEO and influences company strategy, while the VP of Sales typically reports to the CSO.
When comparing CSO to Chief Revenue Officer (CRO), the focus areas differ significantly. The CSO specializes in sales function optimization, while the CRO oversees all revenue-generating activities. The CSO leads sales teams specifically, whereas the CRO manages sales, marketing, customer success, and partnerships. Strategically, the CSO drives sales excellence while the CRO aligns the entire revenue engine.
Core Chief Sales Officer Responsibilities
Modern CSOs manage six critical responsibility areas that define their strategic impact on the organization.

Strategic Sales Planning and Execution forms the foundation of the CSO role. This involves conducting deep competitive research and identifying growth opportunities through comprehensive market analysis. The CSO creates multi-year sales plans with clear milestones and KPIs, designs product launch strategies and market entry approaches, and determines optimal team sizes, territories, and budget distribution for maximum effectiveness.
Sales Team Leadership and Development requires both strategic thinking and hands-on management. The CSO identifies top sales talent and builds diverse, capable teams through strategic recruitment and hiring. They set quotas, track metrics, and implement improvement plans while developing training programs and mentoring emerging sales leaders. Creating a results-driven culture that promotes collaboration and growth becomes essential for long-term success.
Revenue Forecasting and Pipeline Management ensures accurate revenue prediction for business planning and investor relations. The CSO monitors deal flow, conversion rates, and sales cycle length while using data analytics to predict quarterly and annual revenue. They identify potential revenue shortfalls and implement corrective measures while prioritizing high-value deals and optimizing resource allocation.
Cross-Functional Collaboration has become increasingly important as the modern CSO breaks down silos between departments. This includes ensuring lead quality, messaging consistency, and campaign effectiveness through marketing alignment. The CSO provides customer feedback to influence product roadmaps and features while coordinating post-sale activities to drive retention and expansion. Working with finance, legal, and HR to optimize sales processes creates operational efficiency across the organization.
Technology and Data Management represents a critical evolution in the CSO role. Today's CSOs must be comfortable with sales technology and data analysis, including selecting and managing customer relationship management systems and using data to identify trends, optimize processes, and improve performance. They evaluate and implement sales enablement tools while leveraging artificial intelligence for prospecting, lead scoring, and automation. This technology implementation often requires close collaboration with Sales Operations teams who provide the infrastructure and analytical support for data-driven sales processes.
Companies using AI-driven sales tools are 1.3 times more likely to see revenue increases, making technology adoption a critical CSO responsibility. This is where comprehensive data platforms become essential, as managing multiple data sources manually creates inefficiencies and inaccuracies that impact decision-making quality.
Customer Relationship Management shapes how the organization approaches customer relationships at the strategic level. The CSO develops approaches for key accounts and strategic partnerships while ensuring consistent, positive interactions throughout the sales process. They create programs to reduce churn and increase customer lifetime value while maintaining connections with key stakeholders and industry partners.
Essential Skills for Chief Sales Officers
The most successful CSOs combine traditional sales expertise with modern business acumen across several critical skill areas.

Strategic Leadership Skills encompass the ability to see long-term opportunities and create compelling strategies through vision development. Change management becomes crucial as CSOs lead organizational transformation and adapt to market shifts. Complex decision-making with incomplete information and multiple stakeholders requires advanced analytical thinking, while effective communication with boards, investors, and cross-functional teams determines strategic success.
Sales and Revenue Expertise builds on deep understanding of B2B sales cycles, methodologies, and best practices. Revenue optimization involves identifying and implementing strategies to increase deal sizes and close rates. Market knowledge encompasses understanding industry trends, competitive dynamics, and customer behavior, while performance management requires setting realistic targets and developing improvement strategies that drive consistent results.
Technology and Data Proficiency has become non-negotiable for modern CSOs. Advanced knowledge of Salesforce, HubSpot, or similar CRM platforms provides the foundation for data-driven decision making. The ability to interpret sales metrics, identify trends, and make informed decisions separates successful CSOs from their peers. Understanding how to implement and leverage sales technology effectively, combined with leading the adoption of new technologies and processes, creates competitive advantages.
This technological proficiency becomes particularly important when dealing with data fragmentation across multiple systems. Traditional approaches require managing numerous data sources manually, leading to inconsistencies and inefficiencies. Modern CSOs leverage platforms like Databar.ai to access 90+ data providers through a single interface, enabling faster decision-making and more accurate forecasting while reducing operational complexity.
Team Management and Development rounds out the essential skill set through developing sales talent and building leadership pipelines. Setting clear expectations and providing constructive feedback drives performance improvement, while creating environments that promote collaboration, innovation, and results builds sustainable success. Identifying and recruiting top sales professionals ensures the organization has the talent needed to execute strategic objectives.
Chief Sales Officer Salary and Compensation
CSO compensation reflects the critical nature of the role, with significant variation based on company size, industry, and geographic location.
Early-stage startups in Series A/B funding rounds typically offer base salaries ranging from $180,000 to $250,000, with total compensation reaching $220,000 to $350,000. Equity packages often range from 1.5% to 2.5%, reflecting the higher risk and potential upside of these organizations.
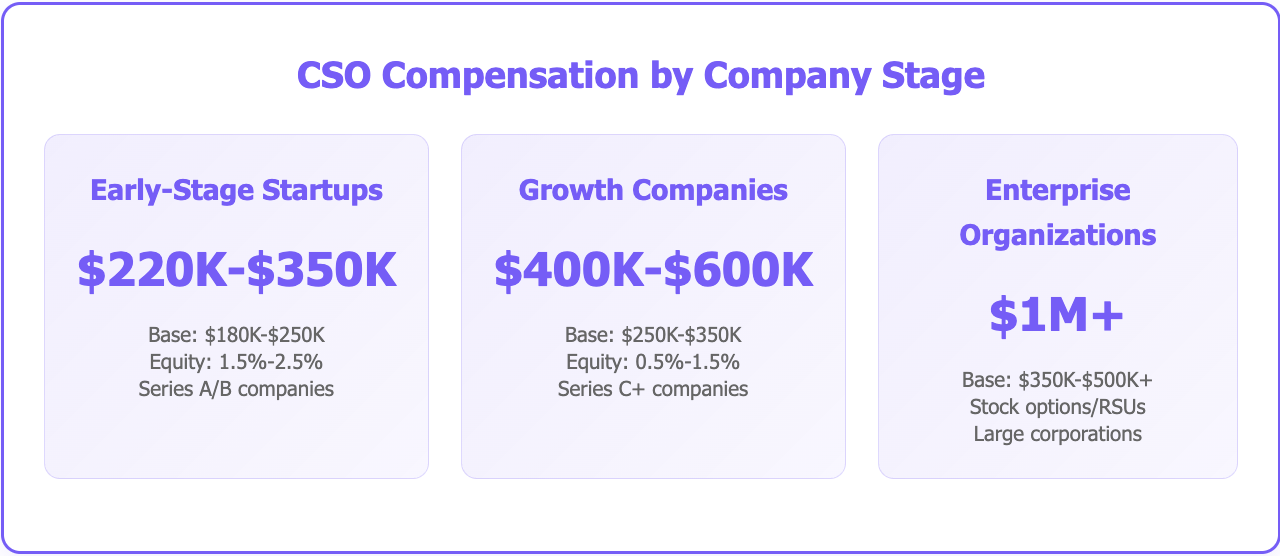
Growth companies in Series C and beyond increase compensation significantly, with base salaries from $250,000 to $350,000 and total compensation reaching $400,000 to $600,000. Equity packages typically range from 0.5% to 1.5%, still providing meaningful upside potential.
Enterprise organizations offer the highest compensation levels, with base salaries from $350,000 to over $500,000 and total compensation exceeding $1,000,000 in many cases. These roles typically include stock options or RSUs rather than direct equity percentages.
Geographic variations create significant differences in compensation levels. High-cost markets like the SF Bay Area, NYC, and Boston command 25-40% premiums over national averages, with higher equity compensation and additional benefits. Secondary markets such as Austin, Denver, and Seattle offer 10-20% premiums over national averages with competitive benefits packages and growing opportunity markets. Other markets tend closer to national averages, often offset by lower cost of living, with remote work opportunities increasing access to top-tier roles.
Performance-based compensation forms a significant portion of total CSO packages. Annual bonuses typically range from 30-50% of base salary tied to revenue targets, while long-term incentives include multi-year equity vesting schedules. Accelerators provide additional compensation for exceeding targets, and retention bonuses offer special incentives for key hires or retention in competitive markets.
The Modern CSO Challenge: Data-Driven Decision Making
One of the biggest challenges facing CSOs today involves making data-driven decisions while managing increasingly complex sales processes. According to Gartner, 65% of B2B sales teams will transition from intuition-based to data-driven decision making by 2026, creating both opportunities and challenges for sales leadership.

Data fragmentation represents a significant obstacle as sales data scattered across multiple systems including CRM, marketing automation, customer success platforms, and various point solutions makes it difficult to get a complete view of the customer journey and sales performance. This fragmentation leads to inconsistent reporting, missed opportunities, and suboptimal decision-making.
Manual data enrichment consumes valuable time as sales teams spend up to 70% of their time on non-selling activities, including manual data entry and research. This inefficiency prevents CSOs from scaling their operations effectively and reduces the time available for high-value activities like relationship building and strategic selling.
Inconsistent data quality creates cascading problems throughout the organization. Poor data quality leads to inaccurate forecasting, missed opportunities, and ineffective sales strategies. CSOs need reliable, up-to-date information to make informed decisions about resource allocation, territory planning, and strategic initiatives.
Limited integration capabilities plague many organizations as they struggle with connecting their various sales tools and data sources. This leads to workflow inefficiencies, reduced productivity, and increased operational costs that impact overall sales performance.
Leading CSOs address these challenges through strategic technology adoption and process optimization. Centralized data platforms provide consolidated data from multiple sources, creating a single source of truth for sales performance and customer insights. Automated enrichment solutions replace manual research and data entry processes, dramatically reducing time spent on administrative tasks while improving accuracy and consistency.
Modern CSOs leverage platforms like Databar.ai to solve these data challenges efficiently. Instead of managing subscriptions to multiple data providers and dealing with various APIs and integration challenges, they access 90+ premium data providers through a single interface. This approach reduces operational complexity while improving data coverage and accuracy, enabling faster decision-making and more precise forecasting.
AI-powered insights help advanced CSOs analyze patterns in their sales data, predict deal outcomes, and identify at-risk opportunities before they become problems. Workflow automation frees up teams to focus on high-value activities like relationship building and strategic selling by handling routine tasks and data flows automatically.
Building High-Performance Sales Teams
The approach to building and leading sales teams has evolved significantly, requiring modern CSOs to adapt their strategies for attracting, developing, and retaining top talent in an increasingly competitive market.
Skills-based hiring has replaced traditional experience-focused recruitment as modern CSOs look beyond years in sales to identify candidates with the right mix of consultative selling abilities, technology proficiency, data analysis capabilities, and customer empathy. Diverse team building reflects research showing that diverse sales teams achieve better results, leading CSOs to prioritize building inclusive teams that reflect their customer base. Remote and hybrid capabilities have become essential as CSOs must build teams that can perform effectively across various work environments.
Continuous learning culture development represents a critical investment, as top-performing sales organizations invest 35% more in training than their peers. CSOs create comprehensive programs including regular skills assessments and development plans, technology training and certification programs, industry knowledge and competitive intelligence updates, and leadership development for high-potential team members.
Data-driven coaching replaces subjective feedback with specific, actionable insights based on actual performance data from conversation intelligence tools and CRM analytics. Cross-functional training ensures sales teams understand how their work connects to marketing, customer success, and product development, creating more effective collaborators throughout the organization.
Performance management and motivation require clear metrics and expectations that align with company goals. Successful CSOs establish transparent performance metrics including revenue targets and quota attainment, activity metrics such as calls, demos, and proposals, quality measures like deal size, cycle time, and win rate, plus customer satisfaction and retention metrics. Recognition and incentive programs beyond basic compensation celebrate both individual and team achievements, creating sustained motivation and engagement.
Technology Stack Management for CSOs
The modern CSO's technology stack requires careful selection and integration of tools that support the entire sales process effectively.

Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems form the foundation of any sales technology stack, storing customer data, tracking interactions, and managing the sales pipeline. Leading options include Salesforce, HubSpot, and Pipedrive, each offering different capabilities and integration options.
Sales enablement platforms help sales teams access content, training, and resources more effectively. Popular solutions like Highspot, Showpad, and Seismic provide centralized content management, training delivery, and performance analytics.
Data enrichment and intelligence tools provide comprehensive information about prospects and customers for informed decision-making. Traditional approaches require multiple subscriptions to various data providers, creating complexity and inconsistency. Modern solutions like Databar.ai consolidate access to 90+ data sources through a single platform, dramatically simplifying data management while improving coverage and accuracy.
Conversation intelligence platforms analyze sales calls to provide insights into what's working and what needs improvement. Tools like Gong, Chorus, and Otter.ai help CSOs understand conversation patterns, identify coaching opportunities, and optimize sales messaging.
Sales analytics and forecasting platforms provide advanced analytics to help CSOs understand trends, predict outcomes, and optimize performance across their sales organization. These tools integrate with CRM systems to provide comprehensive reporting and predictive insights.
Integration and workflow optimization represent the key to successful sales technology adoption. Leading CSOs focus on API integration to ensure all tools can share data effectively, creating a unified view of customers and prospects. User experience considerations drive tool selection, prioritizing intuitive, easy-to-use solutions that reduce training time and increase adoption rates. Automation implementation handles routine tasks through automated workflows, allowing sales teams to focus on high-value activities. Data flow optimization creates systems where information flows automatically between tools, reducing manual data entry and improving accuracy.
The Future of the CSO Role
The CSO role continues evolving as technology advances and buyer behaviors change, with several key trends shaping the future landscape.
Increased focus on customer experience reflects modern buyers' expectations for personalized, seamless experiences throughout their journey. CSOs must ensure their teams deliver personalized communication based on comprehensive customer data, consistent experiences across all touchpoints, proactive support and value delivery, and long-term relationship focus rather than transactional interactions.
AI and automation integration will accelerate significantly. By 2028, over 40% of B2B sales organizations will leverage multiple AI technologies to automate processes and improve decision-making. CSOs must prepare for AI-powered lead scoring and prioritization, automated prospecting and initial outreach, predictive analytics for deal outcomes, and real-time coaching and performance optimization.
Data-driven decision making will become universal as the shift toward analytics-based management accelerates. This requires CSOs to implement comprehensive data strategies, build analytics capabilities within their teams, make decisions based on insights rather than intuition, and continuously optimize processes based on performance data.
Cross-functional leadership reflects the blurring boundaries between sales, marketing, and customer success. Future CSOs will lead revenue operations across multiple functions, coordinate customer experiences end-to-end, collaborate effectively with other executives, and think strategically about the entire customer lifecycle. nderstanding emerging roles like RevOps vs GTM Engineering helps CSOs build effective partnerships with technical revenue operations teams.
How to Become a Chief Sales Officer
The path to becoming a CSO typically involves progressive sales leadership roles combined with strategic business experience and continuous skill development.
Educational backgrounds that support CSO aspirations include bachelor's degrees in business, marketing, or related fields, with MBAs preferred for larger organizations. Sales certifications and continuing education demonstrate commitment to professional development. Industry knowledge encompasses deep understanding of target markets and customers, competitive intelligence and market dynamics, plus product knowledge and value proposition expertise.
The typical career progression follows a structured path from SDR career path andSales Representative through Senior Sales Representative, Sales Manager, Regional Sales Director, VP of Sales, and finally Chief Sales Officer. Each stage typically requires 2-5 years to master the necessary skills and demonstrate consistent results. Key experience areas include direct sales experience with quota responsibility, team leadership and management, P&L responsibility and business management, cross-functional collaboration, and strategic planning and execution.
Skills development focus should emphasize business acumen including financial planning and analysis, strategic planning and execution, market analysis and competitive intelligence, and technology evaluation and implementation. Leadership capabilities encompass team building and talent development, change management and transformation, communication and presentation skills, plus executive presence and influence.
Measuring CSO Success
CSOs face evaluation on both quantitative metrics and qualitative impact on organizational performance and culture.
Revenue metrics form the primary evaluation criteria, including total revenue growth year-over-year, quota attainment across the sales organization, average deal size and sales cycle length, and pipeline health and conversion rates. Team performance indicators include sales rep productivity and quota achievement, employee retention and satisfaction scores, time to productivity for new hires, and career advancement plus internal promotion rates.
Operational excellence measures encompass sales process efficiency and standardization, technology adoption and utilization rates, data quality and CRM hygiene, and cross-functional collaboration effectiveness. Strategic impact evaluation includes market share growth and competitive positioning, customer satisfaction and retention rates, new market or product launch success, and contribution to overall business strategy.
Successful CSOs balance leading indicators such as pipeline generation and velocity, sales activity levels and quality, lead response times and conversion rates, and team engagement and satisfaction scores with lagging indicators including revenue achievement and growth, market share and competitive position, customer retention and expansion, and profitability and margins.
Common CSO Challenges and Solutions
Even experienced CSOs face significant challenges in today's complex business environment, with proven solutions available for the most common issues.
Scaling sales operations as companies grow requires maintaining quality and consistency while expanding capacity. Solutions include implementing standardized sales processes and methodologies, investing in comprehensive training and development programs, using technology to automate routine tasks, and creating clear career progression paths that retain top talent.
Data management and insights challenges persist as organizations struggle with multiple data sources and extracting actionable insights. Effective solutions involve consolidating data sources through comprehensive platforms that provide access to multiple premium data providers, implementing robust CRM systems with strong analytics capabilities, training teams on data interpretation and usage, and creating regular reporting and review processes.
Platforms like Databar.ai address these challenges by providing access to 90+ premium data providers through a single interface, eliminating the complexity of managing multiple data subscriptions while ensuring comprehensive coverage and consistent data quality.
Alignment with other departments requires constant coordination to ensure sales efforts support marketing, product, and customer success objectives. Solutions include establishing regular cross-functional meetings and communication channels, creating shared metrics and objectives, implementing service level agreements between departments, and fostering a culture of collaboration and shared success. This coordination often involves working closely with Director of Business Development roles who manage strategic partnership initiatives that support overall revenue objectives.
Adapting to market changes as markets, customer preferences, and competitive landscapes evolve rapidly demands agile responses. Effective approaches include implementing regular market research and competitive analysis, creating flexible sales processes that can adapt quickly, maintaining close relationships with customers for direct feedback, and building scenarios and contingency plans for different market conditions.
Conclusion: The Strategic Imperative of Modern CSO Leadership
The Chief Sales Officer role has evolved far beyond traditional sales management into a strategic leadership position that drives organizational success. Modern CSOs must combine deep sales expertise with technological proficiency, data analysis capabilities, and cross-functional leadership skills to navigate today's complex business environment effectively.

Looking toward the future, the most successful CSOs will embrace technology, prioritize data-driven decision making, and focus on creating exceptional customer experiences. The integration of AI and automation will continue reshaping the sales landscape, making it essential for CSOs to stay ahead of technological trends while maintaining the human relationships that remain at the heart of successful selling.
Organizations seeking to thrive in today's competitive environment need CSOs who can navigate complexity, drive growth, and build scalable sales operations. The investment in strong sales leadership pays dividends through increased revenue, improved market position, and sustainable competitive advantage.
For aspiring CSOs, the path forward requires continuous learning, broad business experience, and commitment to staying current with evolving best practices and technologies. The role offers significant career satisfaction and financial rewards for those who can successfully lead sales organizations in our rapidly changing business environment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the difference between a CSO and a VP of Sales? A CSO focuses on strategic, company-wide sales initiatives and long-term planning, while a VP of Sales manages day-to-day operations and quarterly targets. CSOs typically have broader authority and report directly to the CEO, while VPs often report to the CSO.
How much do Chief Sales Officers make? CSO salaries range from $200,000 to $500,000+ in base salary, with total compensation reaching $300,000 to over $1,000,000 including bonuses and equity. Compensation varies significantly based on company size, location, and performance.
What skills are most important for a CSO? The most critical skills include strategic leadership, revenue optimization expertise, data analysis capabilities, cross-functional collaboration, and technology proficiency. Modern CSOs must also understand AI and automation tools.
How long does it take to become a CSO? The typical path to CSO takes 15-20 years, progressing through sales rep, manager, director, and VP roles. However, exceptional performers in high-growth companies may advance faster with the right experience and results.
What industries pay CSOs the most? Technology, SaaS, financial services, and healthcare typically offer the highest CSO compensation. These industries value sales leadership highly due to complex sales cycles and high deal values.
Do CSOs need an MBA? While not always required, an MBA is preferred by many larger organizations and can accelerate career progression. Industry experience and proven results are often more important than formal education.
What is the biggest challenge facing CSOs today? The biggest challenge is adapting to rapid technological change while managing increasingly complex sales processes and buyer expectations. Data management and AI integration are particular areas of focus.
How do CSOs measure success? CSOs are evaluated on revenue growth, quota attainment, team performance, pipeline health, and strategic contributions to the business. Both quantitative metrics and qualitative leadership impact are important.
What technology do CSOs need to understand? Modern CSOs should understand CRM systems, sales automation tools, AI and machine learning applications, data analytics platforms, and integrated data solutions like Databar.ai that consolidate multiple data sources.
Is the CSO role growing in importance? Yes, the CSO role is becoming increasingly strategic as companies recognize the importance of sales leadership in driving growth. The complexity of modern sales environments makes experienced CSOs more valuable than ever.
Related articles

Claude Code for RevOps: How Revenue Operations Teams Are Using AI Agents to Fix CRM Data, Automate Pipeline Ops & Build Systems
Using AI Agents to Fix CRM Data and Streamline Revenue Operations for Scalable Growth
by Jan, February 24, 2026

Claude Code for Sales Managers: A Practical Guide to Deal Reviews, Rep Coaching, Pipeline Inspection, and Forecast Prep in 2026
Speed Up Coaching and Forecast Prep with Data You Can Trust
by Jan, February 23, 2026

How to Build a Client Onboarding System in Claude Code for GTM Agencies
How To Cut Client Onboarding from Weeks to Hours with Claude Code
by Jan, February 22, 2026

How to Run Closed-Won Analysis with Claude Code
How Claude Code Turns Your CRM Data into Actionable Sales Strategies
by Jan, February 21, 2026